| Previous Page | | | Next Page |
- Data Merge From Xl To Indesign
- Data Merge Indd
- Data Merge Minecraft
- Data Merge Sas
- Data Merge Indesign Not Working
- Data Merge Illustrator
| Merging SAS Data Sets |
| Merging with a BY Statement |
Merging with a BY statement enables youto match observations according to the values of the BY variables that youspecify. Before you can perform a match-merge, all data sets must be sortedby the variables that you want to use for the merge.
- SAS Merge Datasets Example: Often different data on the same cases are stored in two or more different data sets. For example, you may have two person-level data sets on exactly the same individuals but containing different information on those individuals. To combine the data on those individuals into one data set requires a merge.
- In this step-by-step tutorial, you'll learn three techniques for combining data in Pandas: merge,.join, and concat. Combining Series and DataFrame objects in Pandas is a powerful way to gain new insights into your data.
- Use the mergeactiontype attribute in the sys.dmexecplanattributes dynamic management view to return the type of trigger execution plan used as the result of a MERGE statement. Use SQL Trace to gather troubleshooting data for the MERGE statement in the same way you would for other data manipulation language (DML) statements.
In order to understand match-merging, you must understandthree key concepts:
If the data sets do not have a common variable, then you might be able to use another data set that has variables common to the original data sets to merge them. For instance, consider the data sets that are used in the match-merge examples. The table that follows shows the names of the data sets and the names of the variables in each data set.
| BY variable | is a variable named in a BY statement. |
| BY value | is the value of a BY variable. |
| BY group | is the set of all observations withthe same value for the BY variable (if there is only one BY variable). Ifyou use more than one variable in a BY statement, then a BY group is the setof observations with a unique combination of values for those variables. Indiscussions of match-merging, BY groups commonly span more than one data set. |
| Input SAS Data Set for Examples |
For example, the director of a small repertory theatercompany, the Little Theater, maintains company records in two SAS data sets,COMPANY and FINANCE.
| Data Set | Variable | Description |
| COMPANY | Name | player's name |
| Age | player's age | |
| Gender | player's gender | |
| FINANCE | Name | player's name |
| IdNumber | player's employee ID number | |
| Salary | player's annual salary |
The following program creates,sorts, and displays COMPANYand FINANCE:
The following output displays the data sets. Icons pack for mac os x. Notice that the FINANCEdata set does not contain an observation for Michael Morrison.
| The Program |
Data Merge From Xl To Indesign
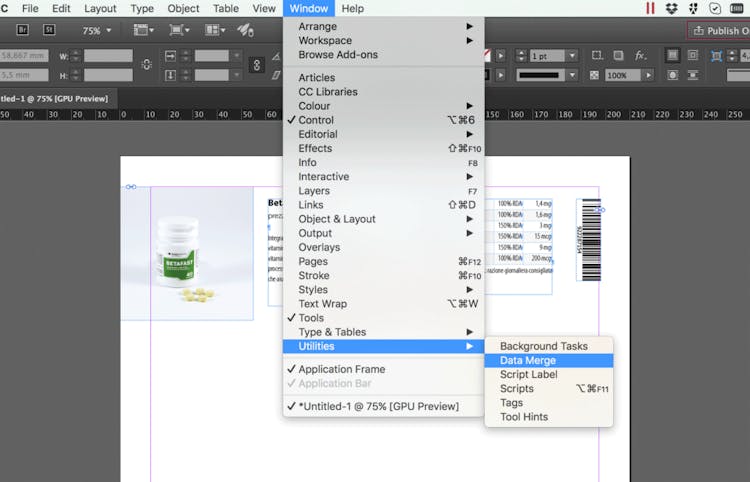
To avoid having to maintain two separate data sets,the director wants to merge the records for each player from both data setsinto a new data set that contains all the variables. The variable that iscommon to both data sets is Name. Therefore, Name is the appropriate BY variable.
The data sets are already sorted by NAME, so no furthersorting is required. The following program merges them by NAME:
Studio one for mac free crack download. The following output displays the merged data set:
| Explanation |
The new data set contains one observation for each playerin the company. Each observation contains all the variables from both datasets. Notice in particular the fourth observation. The data set FINANCE doesnot have an observation for Michael Morrison. In this case, the values ofthe variables that are unique to FINANCE (IdNumber and Salary) are missing.
| Match-Merging Data Sets with Multiple Observations in a BY Group |
Input SAS Data Set for Examples
The Little Theaterhas a third data set, REPERTORY, that tracks the casting assignments in eachof the season's plays. REPERTORY contains these variables:
| Play | is the name of one of the plays inthe repertory. |
| Role | is the name of a character in Play. |
| IdNumber | is the employee ID number of theplayer playing Role. |
The following program creates and displays REPERTORY:
The following output displays the REPERTORY data set:
To maintain confidentiality during preliminary casting,this data set identifies players by employee ID number. However, casting decisionsare now final, and the manager wants to replace each employee ID number withthe player's name. Of course, it is possible to re-create the data set, enteringeach player's name instead of the employee ID number in the raw data. However,it is more efficient to make use of the data set FINANCE, which already containsthe name and employee ID number of all players (see The COMPANY and FINANCE Data Sets). When the data sets aremerged, SAS takes care of adding the players' names to the data set.
Of course, before you can merge the data sets, you mustsort them by IdNumber.
The following output displays the FINANCE and REPERTORY datasets, sorted by IdNumber:
These two data sets contain seven BY groups; that is,among the 23 observations are seven different values for the BY variable,IdNumber. The first BY group has a value of 029-46-9261 for IdNumber. FINANCEhas one observation in this BY group; REPERTORY has two. The last BY grouphas a value of 929-75-0218 for IdNumber. FINANCE has one observation in thisBY group; REPERTORY has three.
The Program
Data Merge Indd
The following program merges the data sets FINANCE andREPERTORY and illustrates what happens when a BY group in one data set hasmore observations in it than the same BY group in the other data set.
Data Merge Minecraft
The resulting data set contains all variables from bothdata sets.
Note: The OPTIONS statement extends theline size to 120 so that PROC PRINT can display all variables on one line.Most output in this section is created with line size set to 76 in the OPTIONSstatement. An OPTIONS statement appears only in examples using a differentline size. When you set the LINESIZE= option, it remains in effect untilyou reset it or end the SAS session.
The following output displays the merged data set:
Data Merge Sas
Explanation
Carefully examine the first few observations in thenew data set and consider how SAS creates them.
Before executing the DATA step, SAS reads thedescriptor portion of the two data sets and creates a program data vectorthat contains all variables from both data sets:
IdNumber, Name, and Salary from FINANCE
Play and Role fromREPERTORY.
Program Data Vector before Reading from Data Sets
SAS looks at the first BY group in each data setto determine which BY group should appear first. In this case, the first BYgroup, observations with the value 029-46-9261 for IdNumber, is the same inboth data sets.
SAS reads and copies the first observation fromFINANCE into the program data vector, as the next figure illustrates.
Program Data Vector after Reading FINANCE Data Set
Download farming simulator 2015 mac. SAS reads and copies the first observation fromREPERTORY into the program data vector, as the next figure illustrates. Ifa data set does not have any observations in a BY group, then the programdata vector contains missing values for the variables that are unique to thatdata set.
Program Data Vector after Reading REPERTORY Data Set
SAS writes the observation to the new data setand retains the values in the program data vector. (If the program data vectorcontained variables created by the DATA step, then SAS would set them to missingafter writing to the new data set.)
SAS looks for a second observation in the BY groupin each data set. REPERTORY has one; FINANCE does not. The MERGE statementreads the second observation in the BY group from REPERTORY. Because FINANCEhas only one observation in the BY group, the statement uses the values ofName (Rudelich , Herbert) and Salary (35000) retained in the programdata vector for the second observation in the new data set. The next figureillustrates this behavior.
Program Data Vector with Second Observation in the BY Group
SAS writes the observation to the new data set.Neither data set contains any more observations in this BY group. Therefore,as the final figure illustrates, SAS sets all values in the program data vectorto missing and begins processing the next BY group. It continues processingobservations until it exhausts all observations in both data sets.
Program Data Vector before New BY Groups
| Match-Merging Data Sets with Dropped Variables |
Now that casting decisions are final,the director wants to post the casting list, but does not want to includesalary or employee ID information. As the next program illustrates, Salaryand IdNumber can be eliminated by using the DROP= data set option when creatingthe new data set.

Note: The difference in placement of thetwo DROP= data set options is crucial. Dropping IdNumber in the DATA statementmeans that the variable is available to the MERGE and BY statements (to whichit is essential) but that it does not go into the new data set. Dropping Salaryin the MERGE statement means that the MERGE statement does not even read thisvariable, so Salary is unavailable to the program statements. Because thevariable Salary is not needed for processing, it is more efficient to preventit from being read into the PDV in the first place.
Data Merge Indesign Not Working
The followingoutput displays the merged data set without the IdNumber and Salary variables:| Match-Merging Data Sets with the Same Variables |
You canmatch-merge data sets that contain the same variables(variables with the same name) by using the RENAME= data set option, justas you would when performing a one-to-one merge (see Performing a One-to-One Merge on Data Sets with the Same Variables).
If you do not use the RENAME= option and avariableexists in more than one data set, then the value of that variable in the lastdata set read is the value that goes into the new data set.
| Match-Merging Data Sets That Lack a Common Variable |

You can name any number of datasets in the MERGE statement. However, if you are match-merging the data sets,then you must be sure they all have a common variable and are sorted by thatvariable. If the data sets do not have a common variable, then you mightbe able to use another data set that has variables common to the originaldata sets to merge them.
For instance, consider the data sets that are used inthe match-merge examples. The table that follows shows the names of the datasets and the names of the variables in each data set.
| Data Set | Variables |
|---|---|
| COMPANY | Name, Age, Gender |
| FINANCE | Name, IdNumber, Salary |
| REPERTORY | Play, Role, IdNumber |
These data sets donot share a common variable. However,COMPANY and FINANCE share the variable Name. Similarly, FINANCE and REPERTORYshare the variable IdNumber. Therefore, as the next program shows, you canmerge the data sets into one with two separate DATA steps. As usual, you mustsort the data sets by the appropriate BY variable. (REPERTORY is already sortedby IdNumber.)
In order to merge the three data sets, this program
sorts FINANCE and COMPANY byName
merges COMPANY and FINANCE into a temporary dataset, TEMP
sorts TEMP by IdNumber
merges TEMP and REPERTORY by IdNumber.
Data Merge Illustrator
| Previous Page | | | Next Page | | | Top of Page |
